Self-control is the ability to control our feelings, emotions, and reactions. For example we need self-control to stop ourselves from doing something we want but shouldn’t like using our phone at work or eating too much candy.
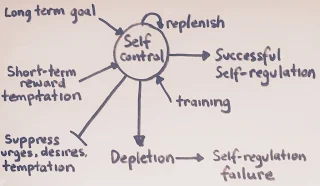 |
| Self-control |
Psychologists typically define self-control by
- The ability to control behaviors to avoid temptations and achieve goals
- The ability to delay gratification and resist unwanted behaviors or urges
- A limited resource that can be depleted
Scientists continue to study the importance of Self-control means choosing what's right even when it's hard, like not eating too much candy or staying off your phone when you should be working.
Types of Self-Control
There are three primary types of self-control:
Impulse control
Refers to the ability to manage urges and impulses. People who struggle with impulse control may act first without thinking about the consequences of their actions.
Emotional control
Refers to the ability to regulate emotional responses. Someone who struggles with emotional control may find it hard to manage strong emotions. They may overreact, experience lasting bad moods, and get overwhelmed by the intensity of their feelings.
Movement control
Refers to the ability to control how and when the body moves. A person who has difficulty with movement control may experience restlessness and find it difficult to remain still.
A self-controlled person exhibits a great deal of willpower and personal control. They don't act impulsively and can regulate their emotions and actions effectively.
Importance of Self-Control
How important is self-control in your day-to-day life? A Stress in America survey conducted by the American Psychological Association (APA) found that 27% of respondents identified a lack of willpower as the primary factor keeping them from reaching their goals. The majority of people surveyed (71%) believed that self-control can be both learned and strengthened.
Examples of Self-Control
Setting goals to exercise regularly, eat a balanced diet, be more productive, give up bad habits, and save money are just a few actions requiring self-control. More examples of self-control include
- Avoiding social media when you are at work so that it doesn't hurt your productivity
- Not purchasing something you want because you are trying to stick to a budget
- Skipping sweet treats because you are trying to reduce your sugar intake
- Managing your emotional response when someone does something that makes you feel angry or upset
Health Benefits of Self-Control
Self-control is also important for maintaining healthy behaviors. What you eat for breakfast, how often you work out, and whether you have a consistent sleep schedule are all decisions that can be affected by your levels of self-control.
Researchers have found that self-control can have a number of potential influences on health and well-being. One longitudinal study found that adults who had greater self-control in childhood were less likely to have:
- Airflow obstruction
- Elevated inflammation
- Metabolic abnormalities
- Periodontal disease
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Substance dependence or addiction to tobacco, alcohol, or cannabis
8 Easy Ways for Self-Control
1. Find more motivation.
Motivation is important in honing self-control skills. Figuring out what motivates you the most is key to accomplishing your goals. Otherwise, what is all this work for? When you look at the bigger picture instead of every detail needed to cross the finish line, you'll find yourself more motivated to get things done.
For example, when working on a long-term project, it's easy to get frustrated by the many small steps, meetings, and approvals required to finish it. Instead, periodically reminding yourself and others on the team of the end goal can help promote motivation.
2. Get a good night's sleep.
Medical News today sleep deprivation impacts our brain function, specifically the prefrontal cortex, which handles reasoning, and the amygdala, which regulates emotions.
Executives and managers should keep this in mind: the more you push employees to work extra hours and answer messages and calls all the time, the more likely employees will be stressed and unhappy. As a result, they may end up cutting corners and engaging in unethical behavior. Do you encourage your team to prioritize sleep? Do you set a good example? Tired workers are not good for business. Take note of when employees are overworked, and encourage them to openly communicate about it so you can support them accordingly.
3. Self-regulation to improve self-control.
Popular views of self-control are that we should try to control impulses, fight temptations, and actively exercise willpower. But how do you do it? Self-regulation is a great way to increase self-control because it helps you take control of your feelings and actions. Someone who lacks self-regulation can have difficulty dealing with stress, anger, or anxiety. According to a Verywell Mind article, self-regulation helps you better connect to your values and communicate what you need. This can help you feel more at ease.
4. Exercise to increase self-control.
Do you find yourself with no time to exercise? There's good news for you. Short bouts of moderately intense exercise can help boost your self-control. No matter how busy you are, plan to include a short burst of exercise in your daily routine. Take note of how you feel after exercise, and you may find you have more energy throughout the day.
5. Get digital self-control support.
Accountability is key. There are many ways to outsource self-control support, including apps that you can download to your phone. They can be helpful when meeting a work deadline, ensuring that you never miss a workout, and keeping track of your meals and spending.
6. Understand your emotional intelligence.
Emotional self-control, or impulse control, starts with understanding emotional intelligence. Knowing yourself can help you manage your emotions and impulses. For example, do you react impulsively to issues? Do you pause to listen to others' feedback? Are you able to stay composed and positive in stressful circumstances? Can you exercise patience in annoying situations? The ability to keep disruptive emotions and impulses in check is the mark of a seasoned leader.
7. Avoid decision fatigue.
Self-control has important implications for good decision-making. Decision fatigue harms these abilities. For example, some people prefer not to make a decision at all, while others may make impulsive or irrational decisions. If possible, avoid making important decisions at the end of the day when your brain is exhausted. "Sleeping on it" can be very helpful. Additionally, automation is your friend. Put at least some aspects of life on default so you have less decisions to worry about. That can mean using apps or simple decisions you make for yourself in advance. Steve Jobs, for example, always dressed in jeans and black turtlenecks. See how you can simplify decision-making with some simple hacks.
8. Set SMART goals.
You can find yourself losing self-control if the task at hand seems unbearable. Setting actionable SMART goals can help you avoid being overwhelmed. "SMART" goals are specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-bound. Setting achievable and realistic goals can help you build discipline to complete everyday tasks in both your personal and professional life. Accomplishing your dreams, no matter the size, will result in higher motivation and increased self-control moving forward.
